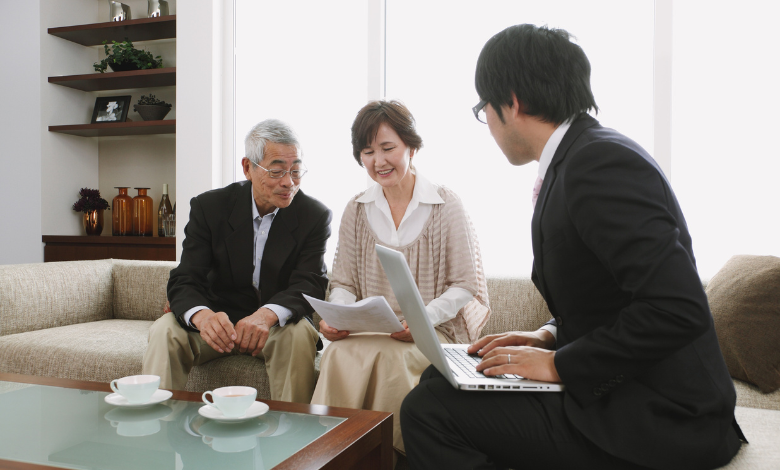
Elder law for dummies explained in clear, simple steps. Discover rights, benefits, estate planning tips, and essential protections for seniors.
Still, confusing, or indeed a little scary, If elder law feels inviting. When I first stepped into this world, it felt like I was trying to read a book written in a language I did not speak. There were strange terms, complicated rules, and endless what ifs that made my head spin. And grounded on what people search online, especially the expression elder law for dummies, utmost people feel the same way. That’s exactly why I wrote this companion. Suppose of it as the freshman-friendly roadmap I wish someone had handed me times ago simple, clear, and completely judgment-free.
What Elder Law Actually Is (Explained in Simple Words)
Before we dive into the details, let’s launch with the simplest possible description. Elder law is the area of law that helps aged grown-ups and their families plan for healthcare, plutocrat, long- term care, and decision- making as they progress. That’s it nothing complicated, nothing intimidating. You can suppose of elder law as a defensive toolbox filled with documents and strategies that keep your loved one safe, supported, and prepared for the times ahead. rather of viewing it as a legal mountain to climb, imagine it as a practical companion that removes stress and brings clarity.
Why Elder Law Matters More Than Most Families Realize
I did not appreciate the importance of elder law until life forced me to. When a close family member suddenly needed long-term care, everything became chaotic. No one knew what documents were needed. No one knew the costs involved. And instead of focusing on care and comfort, we found ourselves drowning in paperwork, rushing to make decisions, and scrambling to figure out what came next. It was emotional, stressful, and completely avoidable.
That’s when I learned the real variety of elder law is lower about lawfulness and further about readiness. It ensures families are not blindsided. It gives favoured bones quality. And it makes delicate transitions far smoother. However, clarity, and peace of mind, If you start planning early indeed when everything seems fine you give yourself options.
The 7 Core Areas of Elder Law (Broken Down Simply)
To make elder law easier to understand, imagine it as a house with seven apartments. Each room has a purpose, and together they produce a safe, well- planned home for your loved one’s future. Let’s walk through each room one by one.
1. Estate Planning
This is the part most people have heard about choices, trusts, and naming who gets what when someone passes down. But it’s further than just means. Estate planning decides who’s in charge, how effects will be handled, and how to help gratuitous conflicts. suppose of a will as a roadmap. Without it, family members end up driving in circles with no directions.
2. Long-Term Care Planning
This room deals with planning for nursing homes, in- home caregivers, supported living, and the costs that come with them. Since long- term care can be thousands of bones a month, this area helps families prepare financially and emotionally so the burden does not fall suddenly on anyone.
3. Medicaid Planning
Medicaid is an important tool for covering long- term care, but it comes with strict rules. Families frequently make expensive miscalculations trying to qualify on their own. Elder law attorneys help navigate this maze, icing plutocrat is defended and eligibility is handled rightly.
4. Guardianship and Conservatorship
Still, the court may appoint a guardian, If someone becomes unfit to make opinions and there are no legal documents in place. While this is occasionally necessary, it’s generally the last resort because it’s long, precious, and frequently emotional. Planning ahead helps avoid this outgrowth.
5. Powers of Attorney
These documents allow someone you trust to make financial or medical decisions if you ca not. Think of powers of attorney as your backup decision-makers. Without them, emergencies turn into legal emergencies.
6. Elder Abuse Protection
Unfortunately, seniors can be vulnerable to financial, emotional, or physical abuse. Elder law includes legal protections to prevent exploitation and ensure older adults stay safe.
7. Special Needs and Disability Planning
If your loved one has a disability or you’re caring for someone who does this, help set up long-term financial and care arrangements to support them far into the future.
When You Should Consult an Elder Law Attorney
Most families wait too long to talk to an elder law attorney. They wait until a crisis happens, a sudden illness, a dangerous fall, a hospital discharge that says you need round-the-clock care. But the truth is, elder law works best when you start planning early.
A good rule of thumb is to begin your elder law planning when the aging process begins, not when it becomes an exigency. That might mean starting the discussion when a parent turns 60, when they retire, or when they start showing early health changes. Meeting with a professional early gives you further choices, further protection, and far smaller last- nanosecond surprises.
Real-Life Examples That Make Everything Clear
To make this easier to understand, here are a few simple scenarios that show just how important elder law planning really is.
The Long-Term Care Surprise
Maria’s mother had been healthy her whole life until she suddenly needed full-time nursing home care. The cost was over $7,000 per month. With no planning done, the family was forced into stressful financial decisions and rushed paperwork. A little early elder law guidance could have prevented that panic.
The Property Transfer Problem
David thought he was doing the right thing by transferring his house to his daughter so she would not have to deal with it later. But he did not understand that transferring property incorrectly can delay or destroy Medicaid eligibility. His one well-intentioned action caused complications that an attorney could have prevented.
The Guardianship Emergency
John developed cognitive issues and could no longer make decisions. His family had no power of attorney in place, so they had to go to court to petition for guardianship. The process was long, expensive, and emotionally draining and completely avoidable if documents had been prepared earlier.
A Simple Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
If elder law feels huge and overwhelming, here is a calming, simple path to follow. This step-by-step guide takes the confusion out of everything.
Step 1: Understand Your Loved One’s Needs
Start by assessing their health, living situation, financial stability, and support system. This will help you know what type of planning you need.
Step 2: Organize Essential Documents
Gather things like identification, bank statements, insurance policies, medical records, and property deeds. Being organized will save you time and stress.
Step 3: Create or Update Key Legal Documents
This includes the will, power of attorney, and healthcare directive. These are the foundation of elder law planning and should be completed as early as possible.
Step 4: Build a Long-Term Care Plan
Explore care options, compare costs, and understand how insurance or Medicaid may help. Planning for care early prevents emotional and financial surprises.
Step 5: Meet With an Elder Law Attorney
Even a single consultation can help you avoid mistakes, save money, and get personalized guidance. Think of an elder law attorney as a guide who helps you navigate a path you’ve never walked before.
The Beginner-Friendly Elder Law Checklist
Here is a simple checklist you can save or screenshot. It’s one of the most helpful tools you’ll use on this journey.
- Will or trust
- Financial power of attorney
- Healthcare directive or medical power of attorney
- A long-term care strategy
- A list of assets and important documents
- Medicaid planning (if needed)
- Safety and elder abuse prevention plans
Completing this checklist puts you ahead of most families.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting Elder Law Planning
Elder law is full of pitfalls that beginners often fall into. Here are the most common ones and how to avoid them.
Waiting Too Long to Start
The later you begin, the harder it becomes to protect assets and make care affordable.
Not Having Powers of Attorney in Place
This single mistake causes more legal emergencies than anything else.
Transferring Property Without Legal Advice
This can create serious Medicaid issues and financial problems later.
Assuming a Will Is Enough
A will handles only one part of elder law. You still need care planning, healthcare directives, and decision-maker documents.
Not Talking Openly With Family
Avoiding these conversations often leads to confusion and conflict down the line.
Frequently Asked Questions (Beginner Edition)
Do I really need an elder law attorney?
Yes. Even one meeting can save you thousands of dollars and months of stress. They help you avoid mistakes you may not even know exist.
Is elder law the same as estate planning?
Not exactly. Estate planning is part of elder law, but elder law includes long-term care planning, Medicaid, guardianship, and more.
Where should I start if I’m brand-new?
Start with powers of attorney. They prevent the biggest emergencies.
How far in advance should we plan for Medicaid?
Ideally, three to five years before long-term care is needed.
What’s the easiest first step?
Go through the checklist above to get organized and understand what you already have.
A Supportive and Practical Call to Action
Still, you’ve formally taken a huge step toward guarding your loved one’s future and reducing your own stress, If you’ve made it this far. Elder law does not have to feel inviting or confusing. Take this companion, save the roster, organize the documents, and begin with one small step at a time. And when you’re ready for substantiated help, speaking with an original elder law attorney can give you a clear, confident path forward.